
Why study Toxoplasma?
TabulaSynthase, the blog of Whitehead Institute, brings together ideas and perspectives from the Whitehead community and beyond. This guest blog was written by Saima Sidik, a research associate in the lab of Whitehead Institute Member Sebastian Lourido.
Friendships blossom through shared meals, but lunch dates can also provide lifelong companions we never intended to acquire. If lunch includes undercooked meat or unwashed vegetables, there’s a chance that it also includes the single-celled parasite Toxoplasma gondii. An acute T. gondii infection can feel like a mild flu, but the parasite isn’t gone when the infected person feels better — it’s only in stealth mode. Dormant parasites accompany their hosts throughout their lives, usually without causing any symptoms1.
In the Lourido Lab at Whitehead Institute, we study the molecular mechanisms that T. gondii uses to move between host cells, live within them, and switch between its active and dormant forms.
Although T. gondii infections are usually asymptomatic, they’re dangerous to immunocompromised people such as AIDS patients or organ transplant recipients. Dormant parasites can reactivate under these circumstances, causing severe inflammation, including potentially fatal inflammation in the brain. Women should avoid becoming infected during pregnancy, as T. gondii can breach the placenta and reach the developing fetus, resulting in birth defects1,2.
Why do we put so much energy into understanding this parasite that few people can name? I’m compelled to study T. gondii because of its own clinical relevance, and also because its biology translates to related human and veterinary parasites. In particular, we hope to shed light on the plasomodia, which cause malaria, and the cryptosporidia, which cause intense diarrhea that’s dangerous to children3,4. Studying another member of their group, like T. gondii, gives us a better chance of understanding these parasites than trying to apply knowledge obtained from heavily studied organisms, like yeast or fruit flies, which are only distant relatives5. Many experimental techniques are easier to apply in T. gondii than in plasmodia or cryptosporidia, making it a useful model for this group.
Studying a parasite that’s divergent from commonly researched organisms means that I get to think about fascinatingly weird biology, and this aspect of T. gondii research compels me as strongly as improving human health. I see our work in the Lourido Lab as being analogous to the Venter Institute’s global ocean sampling expeditions, during which scientists catalogue the strange organisms that survive under the earth’s most extreme conditions6. We too are explorers, traipsing through the phylogenetic tree to see what oddities we can uncover.
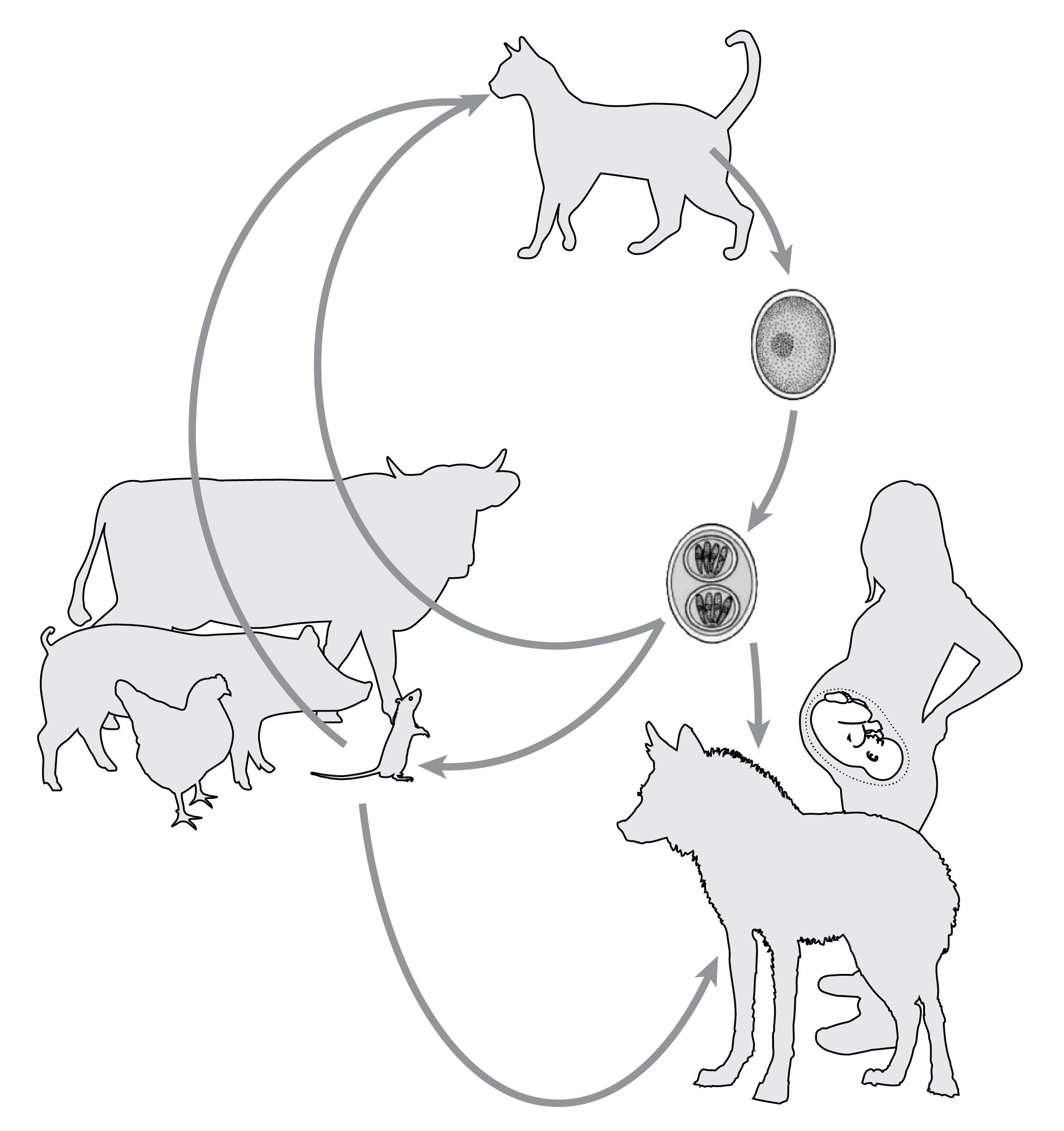 |
| Cats excrete T. gondii in the form of oocysts, which can infect humans, wild animals, rodents and livestock. Livestock can pass infections on to humans who eat undercooked meat. Cats and other wild animals eat infected rodents, which propagates the cycle of infection. |
My research focuses on proteins that let T. gondii invade mammalian cells, and this lets me study an aspect of T. gondii’s biology that makes it odd, even for a parasite. As far as we know, T. gondii can infect any warm-blooded animal, whereas most pathogens only infect one or a few. Many parasitologists think that T. gondii has such a broad host range because it possesses a figurative skeleton key that is sufficient to let it get into any cell. This key is formed from proteins that T. gondii secretes that integrate themselves into its host’s cell membranes, then form openings that let the parasites inside7,8. In contrast, some pathogens, like Plasmodium falciparum, must attach to cells by interacting with molecules that their hosts express on their own cell surfaces before they can secrete invasion proteins. This means that they can only infect cells that have the right surface molecules9. It seems, however, that T. gondii won’t secrete its skeleton key without host cell contact, implying that the host cell is more than just a passive partner in T. gondii infection10. We’re interested in uncovering the molecules that lead to this secretion, and we suspect we’ll learn that host cell membrane composition actually makes some cells easier for T. gondii to invade than others.
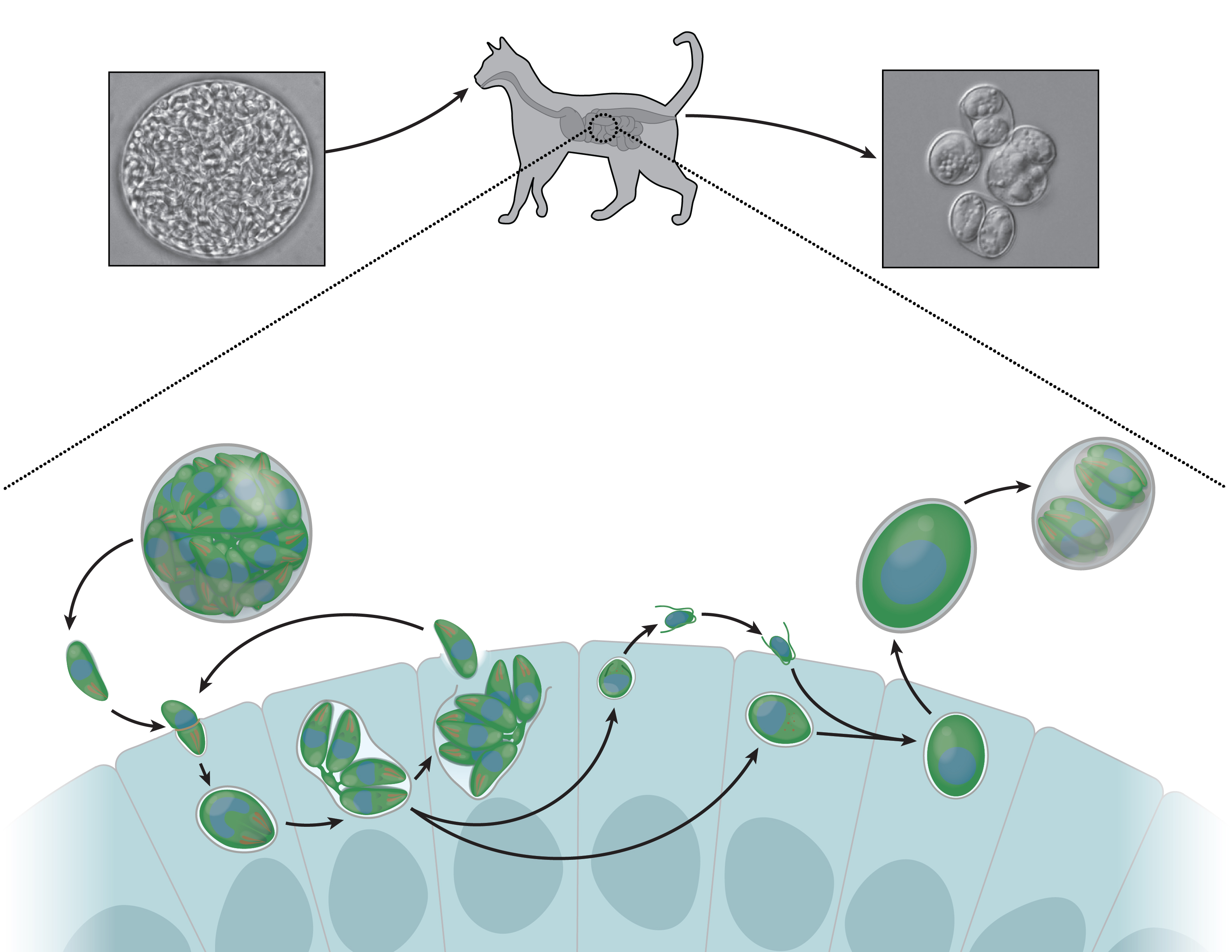 |
| Cats injest T. gondii infected mice, picking up dormant parasites along with their dinner. In the gut, these parasites reactivate and morph into male and female forms. These sexual stages recombine genetically, producing environmentally-stable oocysts that are excreted and then infect humans or other animals. |
Although T. gondii has been found in a wide range of animals, it has a special relationship with cats. In all other hosts, T. gondii reproduces asexually, producing daughter parasites that are genetically identical to their parents. In cats, however, T. gondii morphs into two sexual stages — macrogametocytes (the female form) and microgametocytes (the male form)1. Macro- and microgametocytes are strikingly different, with females taking on a large, ellipsoidal shape11 and males elongating and forming two flagella: long, flexible protrusions that are presumably used for motility1. This part of T. gondii’s lifecycle is full of fascinating unanswered questions. For instance, we don’t know what triggers formation of the micro- and macrogametocytes or why this only happens in cats. After males and females recombine genetically, macrogametes form thick, multi-layered walls comprised of proteins, sugars, and fats. These structures are called oocysts, and they allow the parasites hidden within to survive outside of animal cells. Cats excrete oocysts into the environment, where unsuspecting animals, including humans, eat them and become infected12. Many people have heard that pregnant cat lovers should kindly request that others clean out the litter box, and T. gondii is the reason behind this advice.
T. gondii quickly finds its way to muscle and brain tissue of newly-infected hosts, and here it changes into a slow-growing form that can persist for decades13. Researchers have spent a lot of time looking for behavioral consequences of cerebral T. gondii infection. This is where science fiction fans will be captivated, as researchers have found that rodents lose their innate aversion to the smell of cats after contracting toxoplasmosis. Conferring a loss of fear to rodents is advantageous for parasites, as it increases the odds of cats eating infected mice and therefore producing more oocysts and continuing the cycle of infection14-16. While there are jokes about people who are infected with T. gondii wanting unreasonable numbers of cats, researchers have not reliably detected any psychological consequence of human T. gondii infection. I think, however, that T. gondii’s ability to live in an organ as critical as the brain without causing obvious illness is just as interesting.
The intricate mysteries of T. gondii’s lifecycle fascinate me. I love thinking about how it invades host cells, how it spreads, and how our research can reduce the morbidity caused by it and related parasites. That’s why I study T. gondii.
References
1. Weiss, L. M. & Kim, K. Toxoplasma gondii. (Academic Press, 2014).
2. Auwaeter, P. G. & Spacek, L. A. Toxoplasma gondii. Available at: https://www.hopkinsguides.com/hopkins/view/Johns_Hopkins_ABX_Guide/5405…. (Accessed: 22nd November 2018)
3. WHO | World malaria report 2018. WHO (2018). doi:CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
4. Peletz, R., Mahin, T., Elliott, M., Montgomery, M. & Clasen, T. Preventing cryptosporidiosis: the need for safe drinking water. Bull. World Health Organ. 91, 238–8A (2013).
5. Tree of Life Web Project. Available at: http://tolweb.org/Apicomplexa/2446. (Accessed: 18 December 2018)
6. Global Ocean Sampling Expedition (GOS). J. Craig Venter Institute Available at: https://www.jcvi.org/gos. (Accessed: 18 December 2018)
7. Alexander, D. L., Mital, J., Ward, G. E., Bradley, P. & Boothroyd, J. C. Identification of the moving junction complex of Toxoplasma gondii: a collaboration between distinct secretory organelles. PLoS Pathog 1, e17 (2005).
8. Lebrun, M. et al. The rhoptry neck protein RON4 re-localizes at the moving junction during Toxoplasma gondii invasion. Cellular microbiology 7, 1823–1833 (2005).
9. Weiss, G. E. et al. Revealing the sequence and resulting cellular morphology of receptor-ligand interactions during Plasmodium falciparum invasion of erythrocytes. PLoS Pathog 11, e1004670 (2015).
10. Carruthers, V. B. & Sibley, L. D. Sequential protein secretion from three distinct organelles of Toxoplasma gondii accompanies invasion of human fibroblasts. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 73, 114–123 (1997).
11. Scholtyseck, E., Mehlhorn, H. & Hammond, D. M. Fine structure of macrogametes and oocysts of Coccidia and related organisms. Z Parasitenkd 37, 1–43 (1971).
12. Dubey, J. P., Miller, N. L. & Frenkel, J. K. Characterization of the new fecal form of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Parasitol. 56, 447–456 (1970).
13. Dubey, J. P. & Frenkel, J. K. Cyst-induced toxoplasmosis in cats. J. Protozool. 19, 155–177 (1972).
14. Berdoy, M., Webster, J. P. & Macdonald, D. W. Fatal attraction in rats infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Biol. Sci. 267, 1591–1594 (2000).
15. Vyas, A., Kim, S.-K., Giacomini, N., Boothroyd, J. C. & Sapolsky, R. M. Behavioral changes induced by Toxoplasma infection of rodents are highly specific to aversion of cat odors. PNAS 104, 6442–6447 (2007).
16. Lamberton, P. H. L., Donnelly, C. A. & Webster, J. P. Specificity of the Toxoplasma gondii-altered behaviour to definitive versus non-definitive host predation risk. Parasitology 135, 1143–1150 (2008).
Topics
Contact
Communications and Public Affairs
Phone: 617-452-4630
Email: newsroom@wi.mit.edu


